Agroforestry in Punjab
Punjab, being primarily focused on agriculture, relies on a traditional rice-wheat cropping system that has played a pivotal role in ensuring India's food security. However, certain regions are facing challenges such as nutrient depletion, declining groundwater tables, and an increase in pests and diseases due to overexploitation. These issues underscore the need for a shift away from the current cropping system.
Agroforestry: A Sustainable Alternative in Punjab
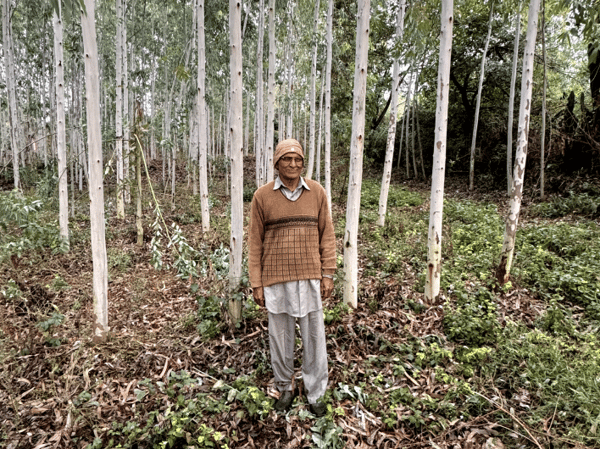
Agroforestry has emerged as a promising alternative to diversify from the conventional rice-wheat rotation. Currently, the agroforestry sector meets over 80% of the country's demand for wood and wood products, with 6% sourced from natural forests and 12% through imports.
In Punjab, this agroforestry initiative not only supplements farm income through carbon revenue but also addresses the socio-economic needs of farmer communities. It aims to empower and uplift their livelihoods, contributing significantly to greater climate resilience. Different tree species, both native and non-native, are cultivated in various agro-climatic zones of Punjab, enhancing the area's biodiversity. Agroforestry meets the rising demand for timber and tree-based products while simultaneously conserving and rehabilitating ecosystems.

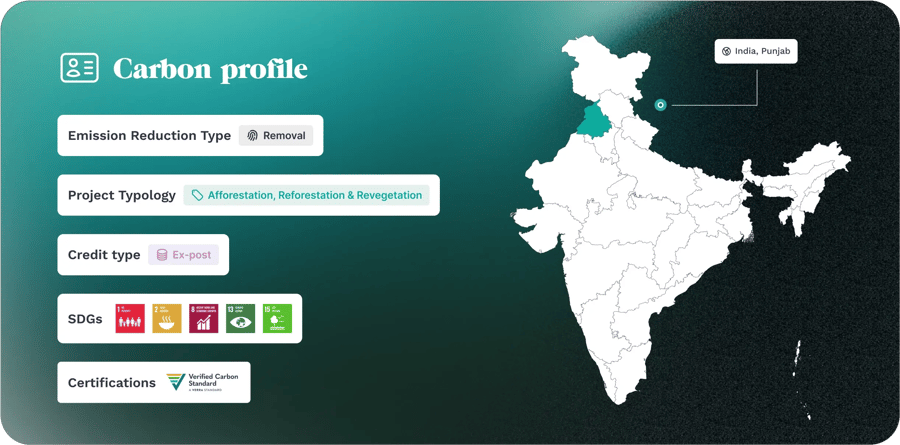
Carbon Projects for Climate-Smart Agriculture
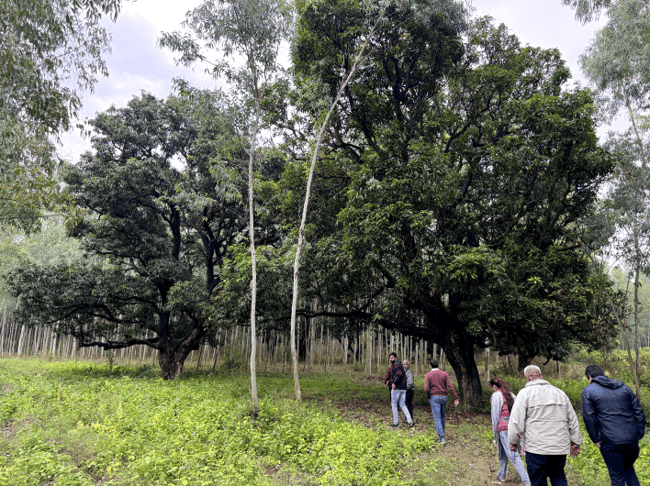
To encourage sustainable agroforestry practices among smallholder farmers in various districts of Punjab, two carbon projects were launched with collaboration from the Department of Forest and Wildlife Preservation of Punjab, alongside key local partners. These projects fall under the afforestation, reforestation, revegetation (ARR) category of the VCS standard. Their primary goals include expanding tree cover beyond forests, contributing to local biodiversity conservation, and enhancing soil health.
For effective project management, clusters will be formed, comprising numerous farmers and community members. Village cluster selection will be done in collaboration with the State Forest Department and Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in the chosen districts. The program not only boosts farmers' income but also propels Punjab towards climate-smart agricultural practices, establishing a sustainable model for future generations.

Contribution to the project by ClimateSeed
An ClimateSeed's contribution plays a vital role in the success of the project and the improvement of the communities involved. By empowering marginalized farmers to generate additional income through carbon credits, the project not only enhances their standard of living but also fosters gender equality by actively involving both men and women. Furthermore, it encourages the establishment of buy-back agreements between farmers and industries, along with local funding options, thereby facilitating the restoration of damaged lands and providing support to farmers with limited resources.

Key Elements
1.8M tCO2
sequestered during project lifetime
8,327 ha
of managed land
3,686
farmers included
Farmers' Testimonials
Project Updates
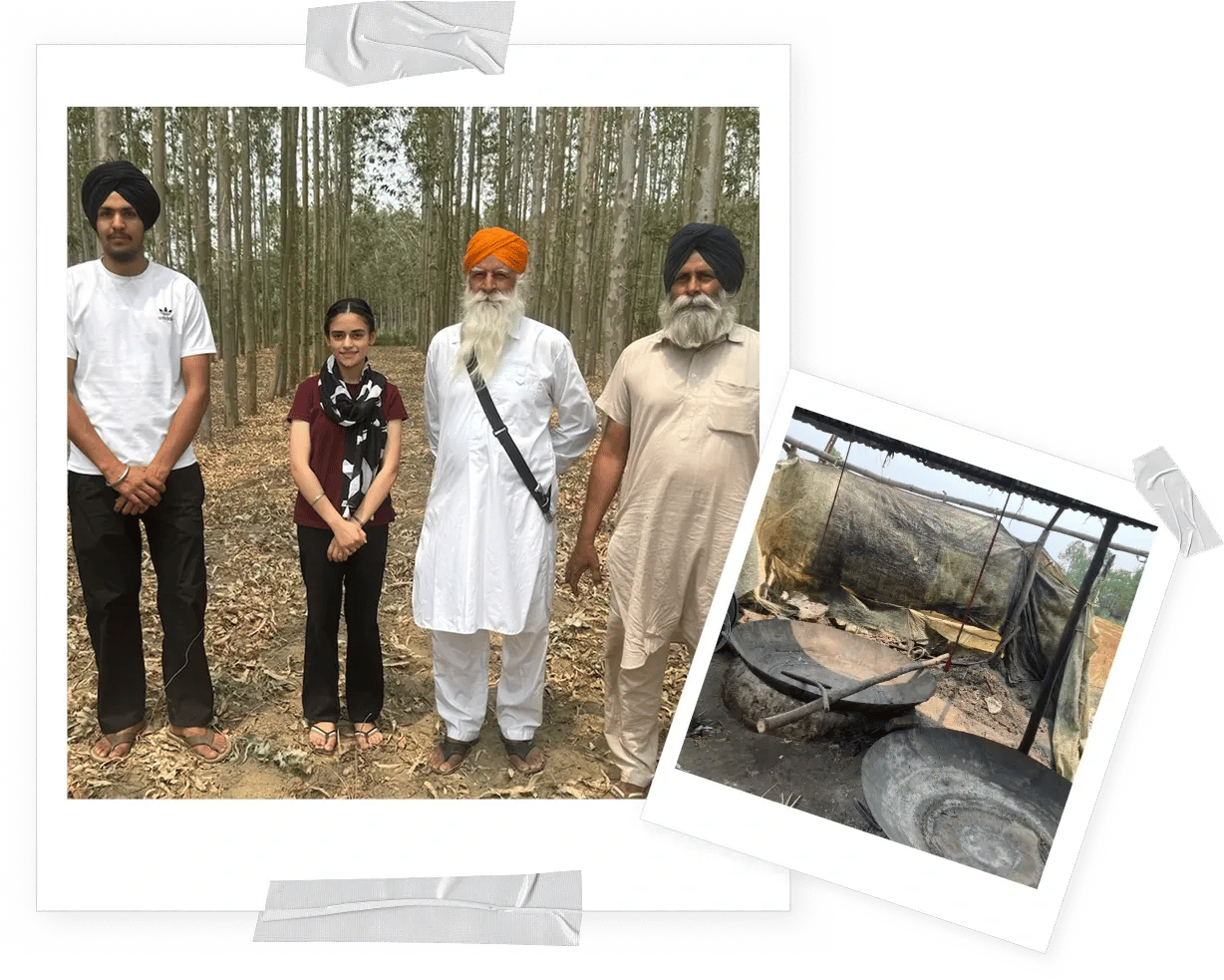
Three Generations, One Frame
By the end of April 2025, we had the opportunity to revisit the project, capturing a heartwarming moment where three generations appear in a single photograph. In another photo, you’ll see unrefined cane sugar this "jaggery" was kindly gifted by the farming family from Punjab.

Interested in more?
Explore further

Climate Change and its Impact on Forests & Protecting Biodiversity through Effective Forest Management
.webp?width=320&height=213&name=forest%20(1).webp)
The Importance of Improved Forest Management Projects (IFM) in the VCM





















