Carbon Credits from Blue Carbon Projects
Carbon credits from blue carbon removal and avoidance projects
What are Blue Carbon projects?
WRC projects involve measures such as re-establishing natural water flows, preventing pollution, and controlling invasive species. These projects contribute to carbon sequestration by restoring wetlands, as wetlands store large amounts of carbon in their vegetation and soils. Additionally, WRC projects help regulate water quality, prevent flooding, support wildlife habitats, and provide recreational and educational opportunities for local communities.
These projects are referred to as carbon removal projects, focusing on the reduction of carbon already present in the atmosphere.
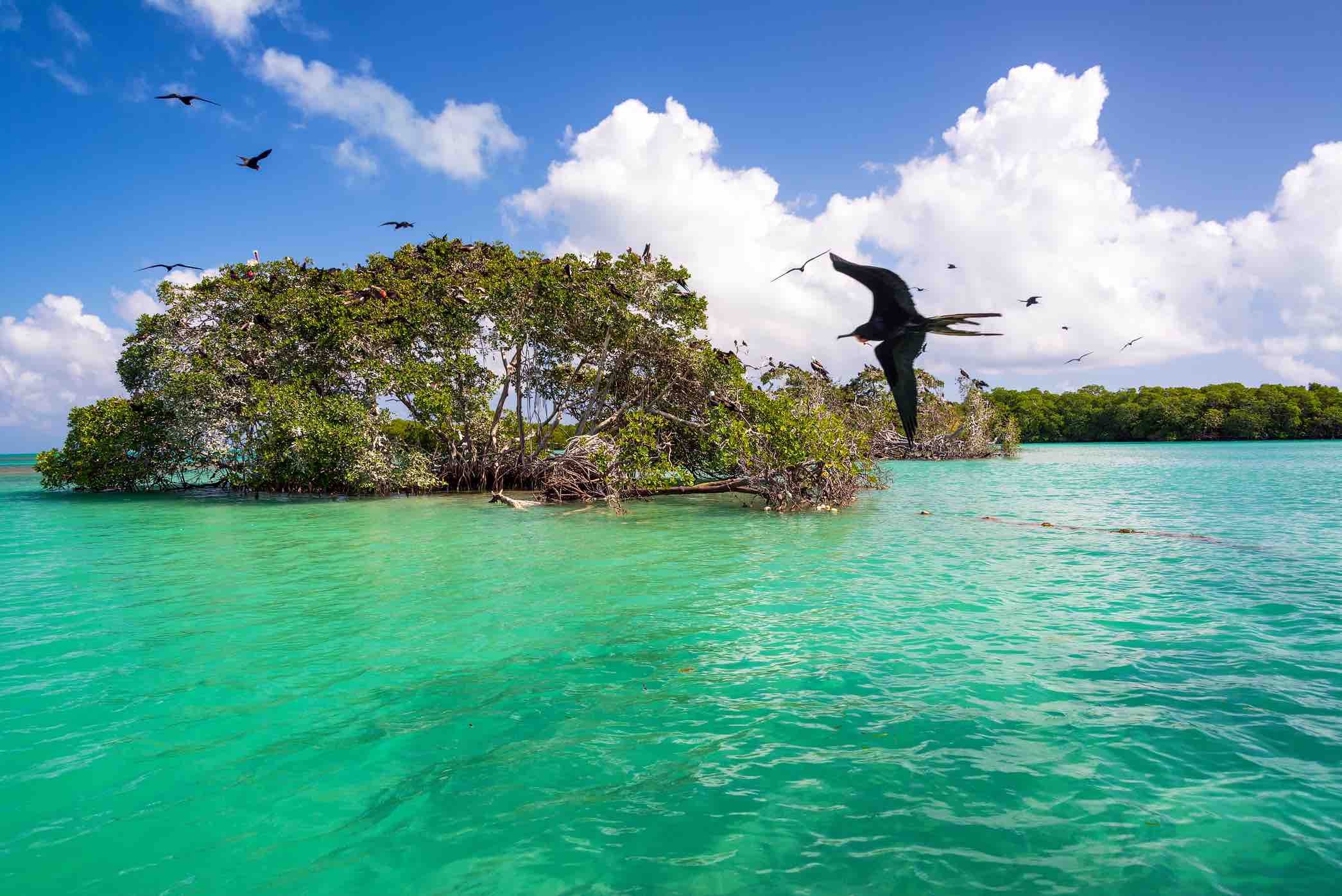

Blue Carbon projects types
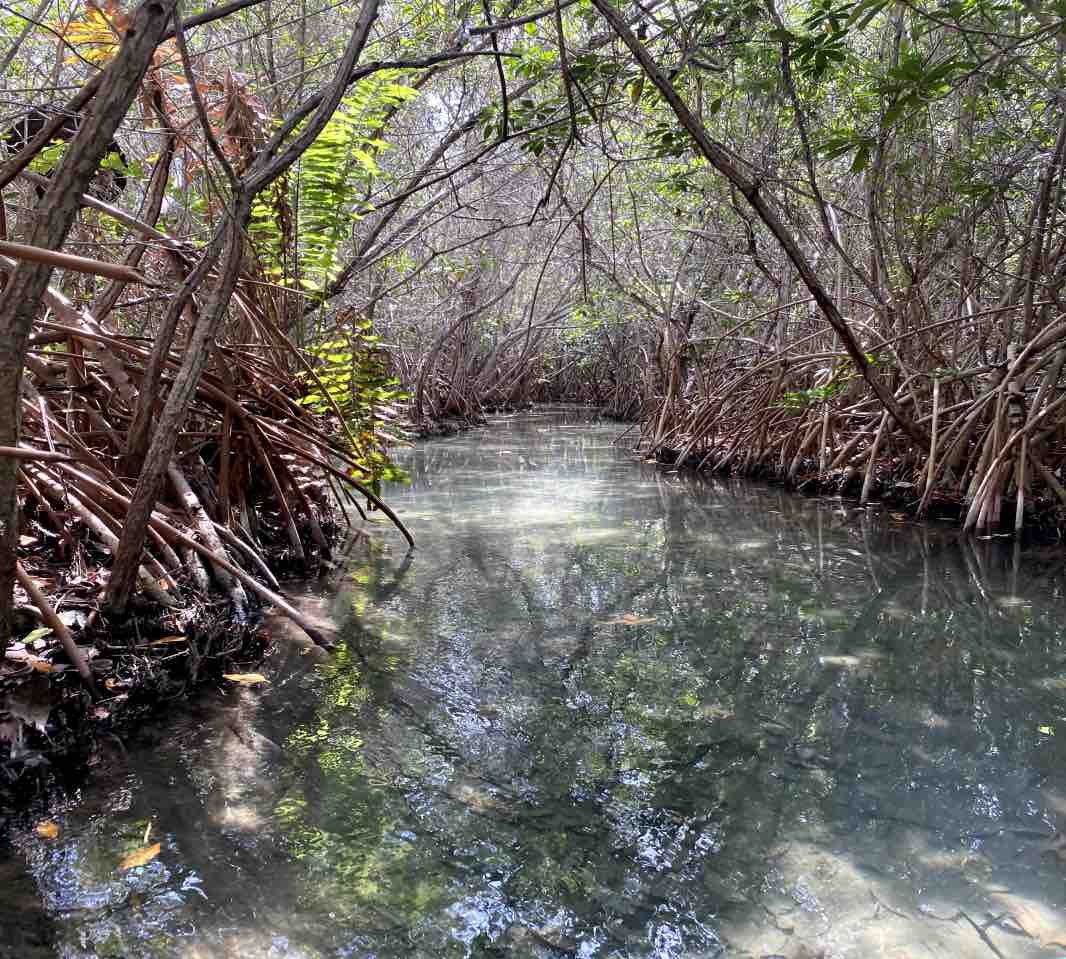
Mangroves
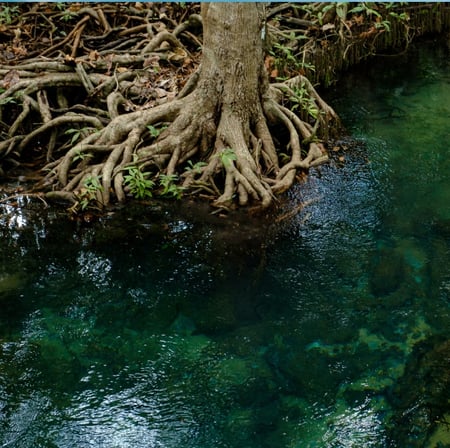

Seagrass and seaweed farming
Seagrass and seaweed farming projects entail the cultivation and management of seagrass meadows and seaweed beds for carbon sequestration. Seagrass meadows sequester carbon through the uptake and storage of carbon dioxide in their leaves and roots. Seaweed beds absorb carbon dioxide from the water column through photosynthesis.
These projects involve the establishment of underwater plots where seagrass or seaweed is cultivated, often utilizing nets or ropes.
By expanding seagrass meadows and seaweed beds, these projects enhance carbon storage, improve water quality, enhance marine biodiversity, and provide habitats for marine organisms.
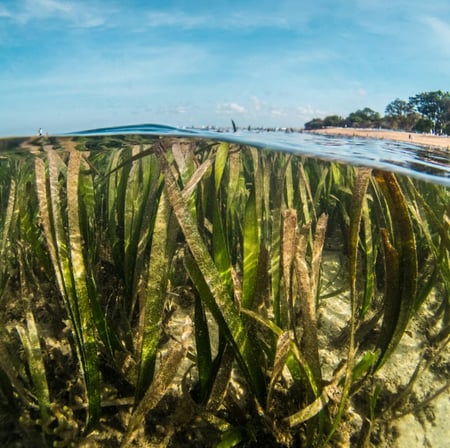

Macroalgae
Macroalgae absorb carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and convert it into organic matter, effectively sequestering carbon. The harvested biomass can be used for various purposes, including biofuel production, food supplements, or as a nutrient-rich source for livestock feed. Macro-algae projects offer high growth rates, scalability, and the potential to provide sustainable alternatives to fossil fuel-based products.
.jpg?width=450&height=448&name=microalgue-min%20(1).jpg)
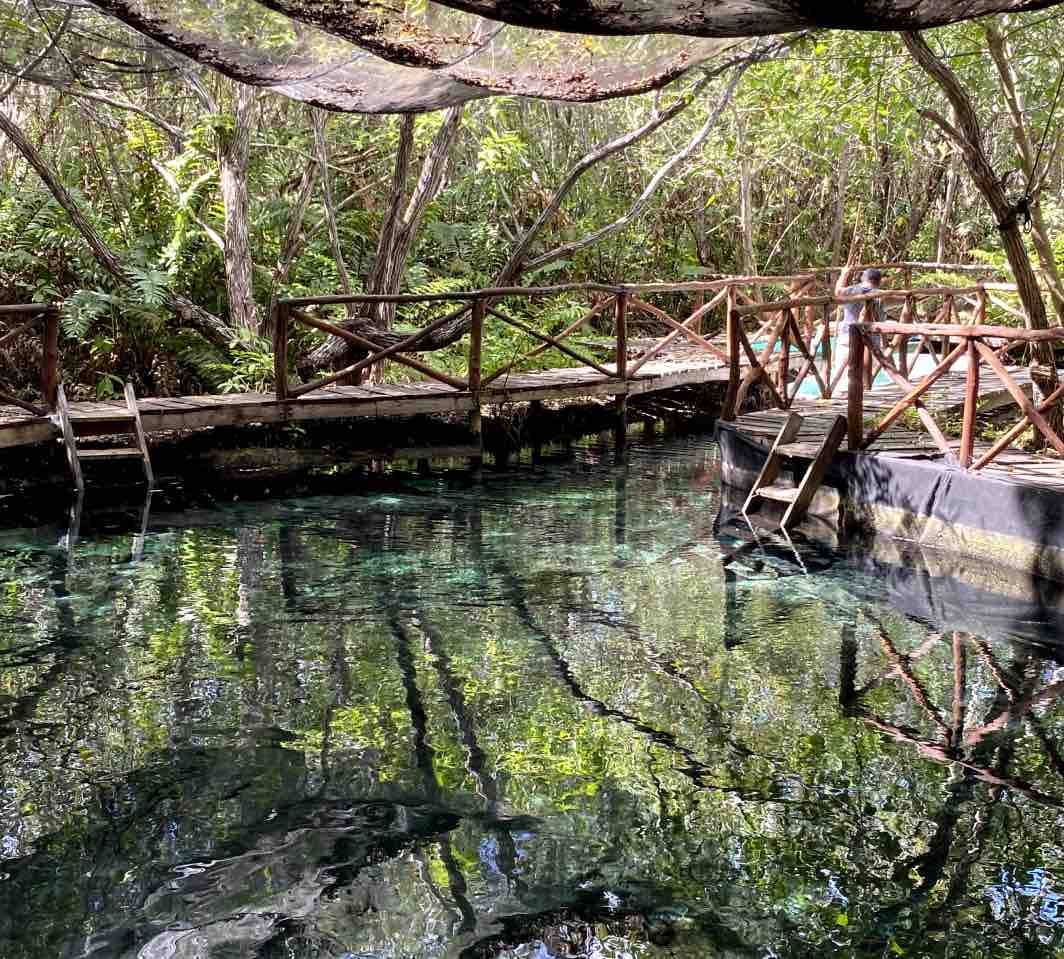
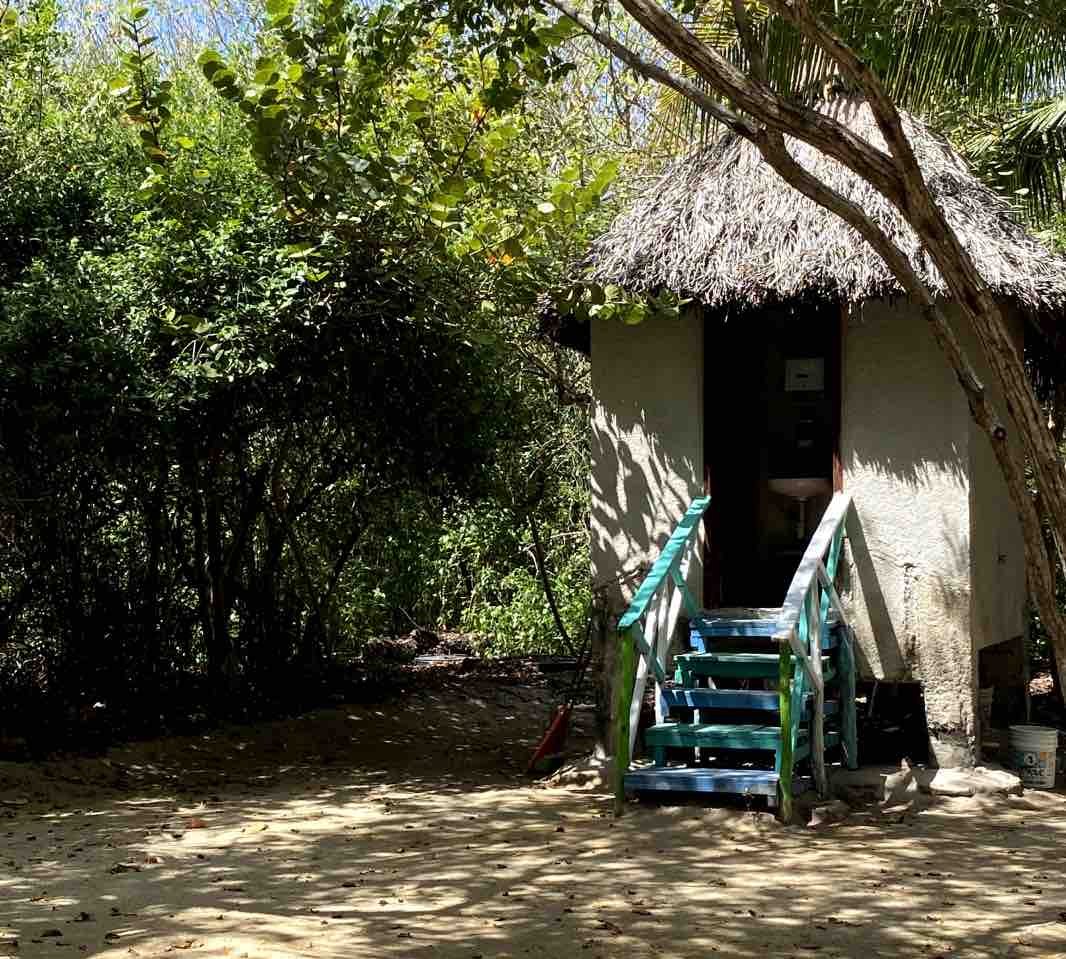
A project example: Mangrove Conservation and Restoration in San Crisanto
Sub-category project typology: Mangroves
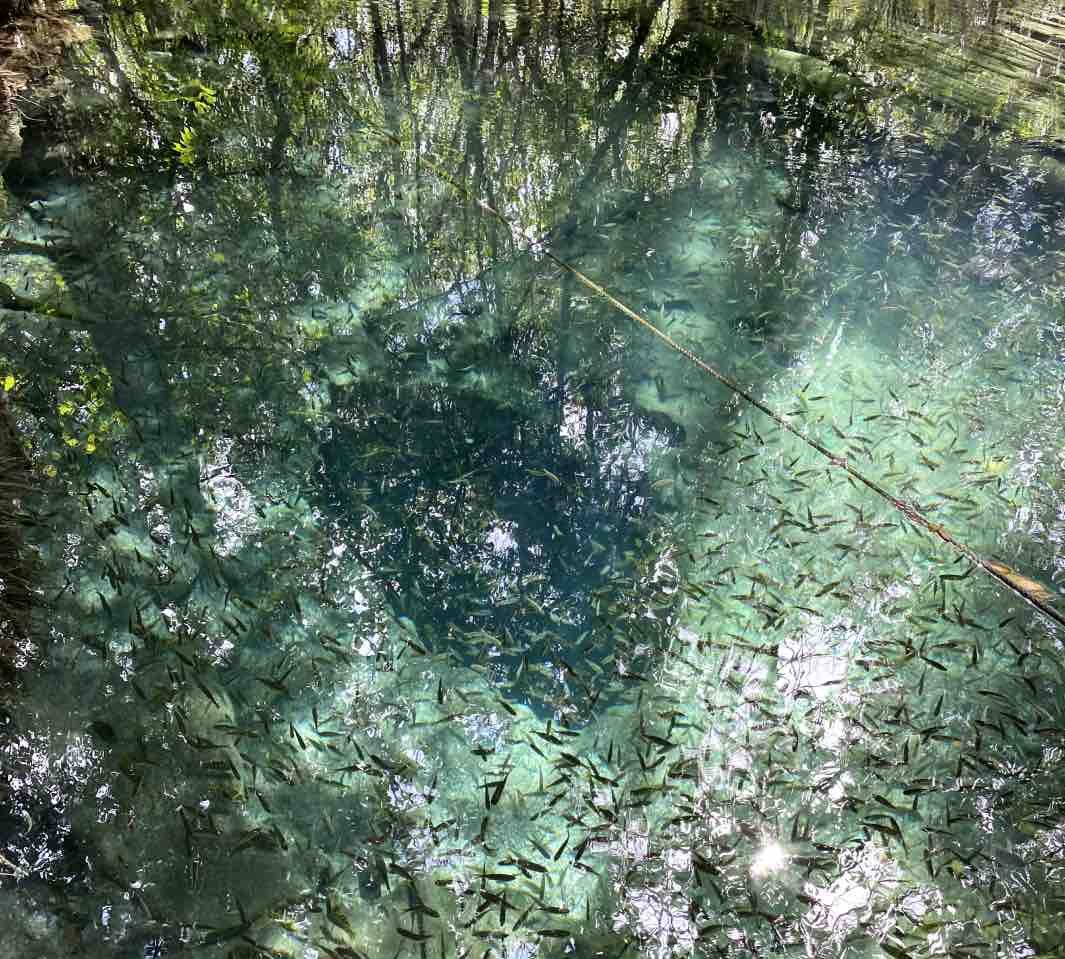
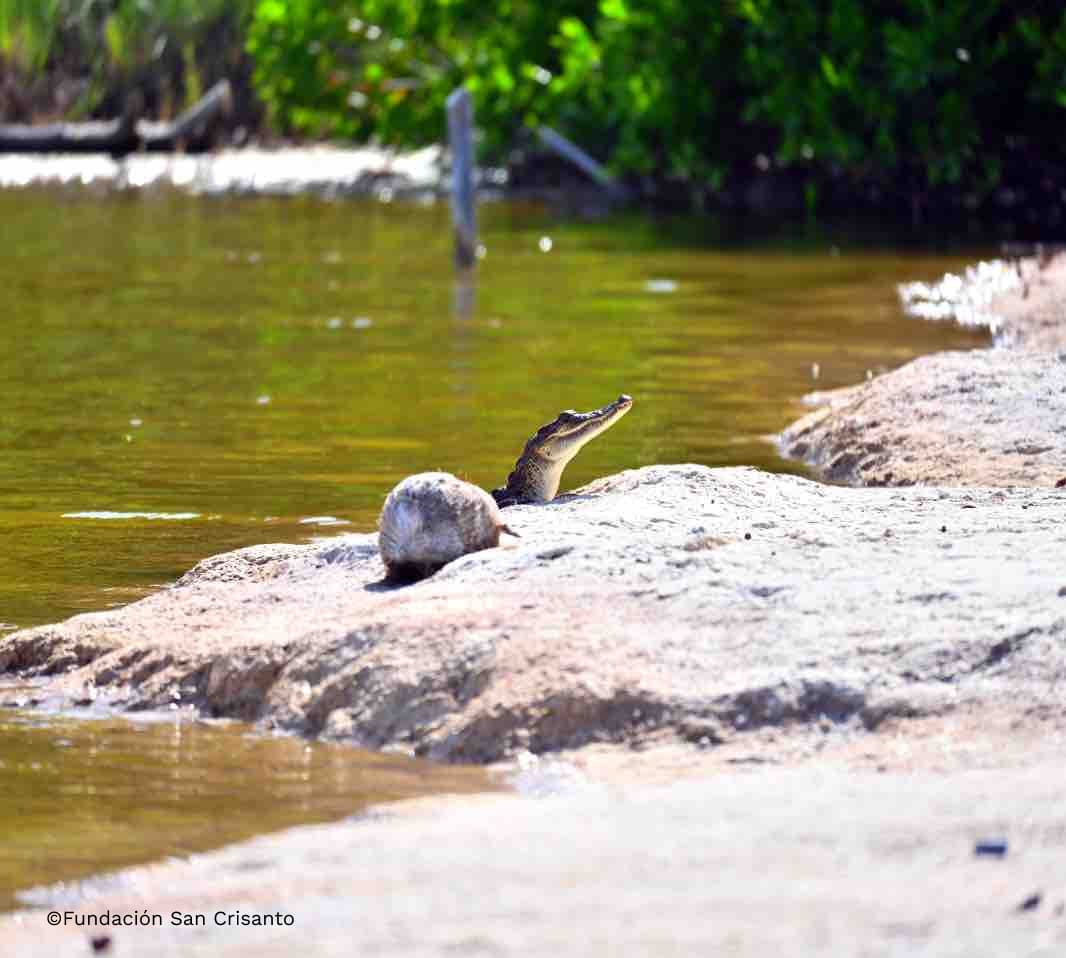
The Mangrove Conservation and Restoration in San Crisanto project covers around 700 hectares of mangrove restoration and conservation as well as numerous activities to preserve biodiversity, sustainably manage natural resources, build community capacity and improve the delivery of healthcare and education services. The primary focus is cleaning and maintaining local canals and cenotes to prevent siltation, which has detrimental effects on the health of local ecosystems. Clear, open canals also enable the community to provide boat trips and wildlife observation excursions to tourists visiting the area, an important source of income. The foundation also undertakes annual evaluations of mangroves and assessments of changes in fish populations, bird species, and crocodiles (Crocodylus moreletii) monitoring to track the impacts of its conservation work.
The Mangrove Conservation and Restoration in San Crisanto project, which was registered under Climate Action Reserve’s Mexico Forest Protocol, is the first of its kind in Mexico. To date, the project includes four reporting periods, and an estimated 35,528 tCO2e have been removed by the project. It is an example of assisted natural regeneration, where local communities intervene to help native vegetation to naturally recover.

60 jobs
generated by reforestation efforts
66% of mangroves
lost in hurricanes and restored since 2017
167 protected species
of resident, migratory and endemic birds
30% of local students
pursue higher education and technical degrees
Where can you find Climate Contribution projects?
Our other projects

Agriculture
Avoidance

Household and Community Devices
Avoidance

Renewable Energy
Avoidance

Waste Management
Avoidance & Removal

Transportation
Removal

Tech-based and Hybrid
Removal

Forestry and Land Use
Removal & Avoidance













